Nullable Non-terminals
In general, a non-terminal can expand to empty string
- example: statement sequence in while language grammar
A sequence of non-terminals is nullable if it can derive an empty string
- this is case iff each non-terminal is nullable
Computing nullable non-terminals:
- empty string is nullable
- if one right-hand side of non-terminal is nullable, so is the non-terminal
Algorithm:
nullable = {}
changed = true
while (changed) {
changed = false
for each non-terminal X
if X is not nullable and either
1) grammar contains rule
X ::= "" | ...
or
2) grammar contains rule
X ::= Y1 ... Yn | ...
and
{Y1,...,Yn} is contained in nullable
then
nullable = nullable union {X}
changed = true
}
Computing First Given Nullable
Computing first(X), given rule X = 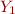 …
… 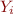 …
… 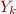
- if
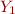 ,…,
,…,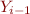 are all nullable, then add first(
are all nullable, then add first(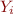 ) to first(X)
) to first(X)
Then repeat until no change, as before.