Control-Flow Graph Definition
Related to traditional notion of flow charts
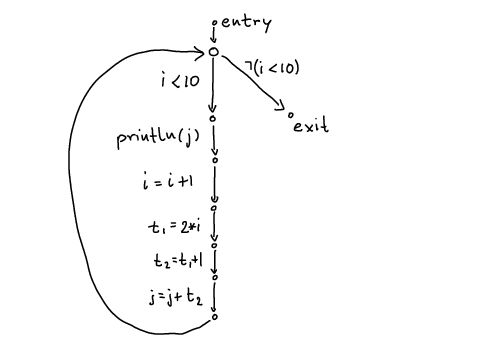
Example program 1:
while (i < 10) { println(j); i = i + 1; j = j +2*i + 1; }
Corresponding control-flow graph:
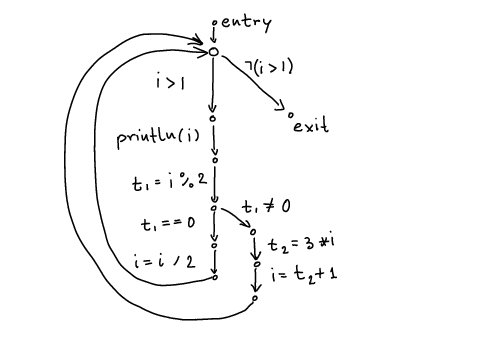
Example program 2:
int i = n; while (i > 1) { println(i); if (i % 2 == 0) { i = i / 2; } else { i = 3*i + 1; } }
Corresponding control-flow graph:
Definition: Control-Flow Graph (CFG) is graph 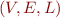 where
where
 is set of CFG nodes, representing program points
is set of CFG nodes, representing program points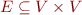 is a multiset of CFG edges (represent how control flows from one point to another)
is a multiset of CFG edges (represent how control flows from one point to another)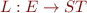 gives a CFG statement for each edge
gives a CFG statement for each edge- statements
- conditions
In the example, what are V,E,L?
atomic expression = variable or a constant
ST statements are simple:
- quadruples: x = y * z (y,z are atomic expression)
- copy
- procedure calls (parameters are atomic)
- relational operators between atomic expressions
Notion of Basic Blocks: straight sequence of nodes (no jumps to or from the middle)