Unification
Unification is the process of solving equations in term algebra, which is the algebra of ground terms, with functions defined as in the Ground Terms section of proof of Herbrand theorem.
The solution process is essentially variable elimination, based on two main properties
Examples
First-order language:
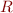 - binary relation symbol
- binary relation symbol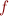 - binary function symbol
- binary function symbol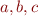 - constants
- constants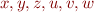 - variables
- variables
Example 1
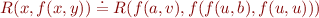
Example 2
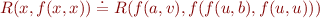
Example 3
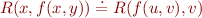
Definition: Unifier of a set 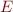 of syntactic equations is a substitution that makes all equations true.
of syntactic equations is a substitution that makes all equations true.
Definition: Composition  of substitutions.
of substitutions.
Definition: A renaming is a substitution which is (a total function and) a bijection on the set of all variables.
Lemma: If 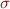 is a unifier for
is a unifier for  and
and  is a substitution, then
is a substitution, then 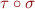 is also a unifier.
is also a unifier.
A unifier is a solution of equations. mgu is the most general solution.
Definition: A most general unifier for  is a unifier
is a unifier  such that if
such that if 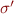 is another unifier, then there exists a substitution
is another unifier, then there exists a substitution  such that
such that 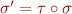 .
.
Algorithm
We next sketch an algorithm for computing mgu.
A set of equations is in solved form if it is of the form 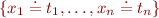 iff variables
iff variables 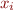 do not appear in terms
do not appear in terms 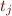 , that is
, that is
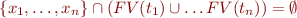
We obtain a solved form in finite time using the non-deterministic algorithm that applies the following rules as long as no clash is reported and as long as the equations are not in solved form.
Orient
Select  where t is not x, and replace it with
where t is not x, and replace it with 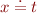 .
.
Delete
Select 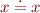 , remove it.
, remove it.
Eliminate
Given  where
where  does not occur in
does not occur in 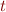 , substitute
, substitute  with
with  in all remaining equations.
in all remaining equations.
Occurs Check
Given  where
where  occurs in
occurs in  , report clash.
, report clash.
Decomposition
Given 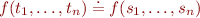 , replace it with
, replace it with 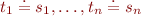 .
.
Decomposition Clash
Given 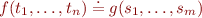 for
for 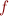 not
not 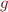 , report clash
, report clash
References
- Unification Theory Chapter in Handbook of Automated Reasoning (also pdf file, see pdf page 10, Rule based approach)
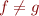
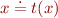 where
where