Code contracts
Spec# (http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/projects/specsharp/) is an example of a static program verifier that uses API contracts to prove program properties. API method contracts usually come in the form of pre- and postconditions:
void p()
requires Pre;
ensures Post;
{
s1;
while (e)
invariant I;
{
s2;
}
s3;
}
where 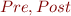 and
and 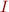 are boolean expressions that are usually written in the same syntax as the code and are pure (have no side-effects). Additionally, they can use
are boolean expressions that are usually written in the same syntax as the code and are pure (have no side-effects). Additionally, they can use
- logical connectives !, &&, ||, =⇒, ⇐⇒
- quantifiers: forall, exists
- additional special keywords e.g. sum, min, max, count, …
Other constructs that may appear:
- result
- method’s return value (used in postcondition)
- old(x)
- value of x before entry to method (used in postcondition)
- modifies x
- frame condition: variable x may be modified in method (usually implicitly no other)
- defaults: modify all or modify none, depending on convention
- assert
- anywhere in code
- run-time checks
- redundant, but useful for code understanding
- assume
- hints for the prover
- “escape” solution (what happens when you use assume(false) in wrong code?)
- object invariants (more complex)
- conditions on object variables that have to hold everywhere
There is also a readable Spec# tutorial and a set of tutorial slides that contain many examples clarifying the use and syntax of many of Spec#’s features.
Further Links for the curious ones
- Spec# uses the Boogie intermediate language and verification tool, which is also used by
- A specification language for Java is the Java Modelling Language (JML) which is used by e.g.
- …
- Jahob: another verification system for Java