Insertion into Doubly-Linked List
(Figure of doubly-linked list of size 3.)
Code:
assume P;
if (first == null) {
first = n;
n.next = null;
n.prev = null;
} else {
n.next = first;
first.prev = n;
n.prev = null;
first = n;
}
assert Q;
Where 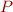 is
is
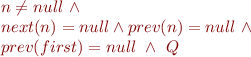
and where  is
is
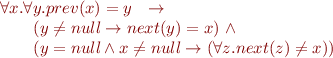
Corresponding Jahob file (call it dll-example.java).
We can check the add method by:
jahob.opt dll-example.java -method Simple.add -usedp cvcl
How can we build a verification conditions for such programs?
- we need to be able to reason about data structures (objects, references, arrays)
Illustration of phases in Jahob system when loop invariants are specified:
- source code
- syntax tree
- jast: simplified statements (use option -jast to see it)
- ast: guarded commands with loops (use option -ast to see it)
- sast (use option -sast to see it):
- eliminating loops with loop invariants by translation to guarded commands (as in Backward VCG with Loops)
- incorporate preconditions and postconditions using assume and assert
- compute weakest precondition with respect to 'true' - this is verification condition (VC)
- simplify VC, split into multiple formulas, eliminate easily provable formulas
- use -v to view the remaining formulas
- use theorem provers to prove the resulting formulas
- some of the provers: cvcl (make symbolic link to cvc3), z3, SPASS, E, Vampire, BAPA, Isabelle (see also –help)
In general, system also deals with:
- specification variables (shorthands and ghost variables)
- loop invariant inference