Homework 4
Due on Monday, 19 November at 10:15am sharp (right before the class).
NOTE: It is your responsibility to ask us if any part of the problem formulation is unclear.
Problem 1
Determine for the following program its output with static and dynamic scoping. Explain the difference, if there is any.
object MyClass {
val x = 5
def foo(z: Int): Int = {
x + z
}
def bar(y: Int): Int = {
val x = 1
val z = 2
foo(y)
}
def main() {
val x = 7
println(foo(bar(3)))
}
}
Problem 2
Consider the following grammar:
E ::= E+E E ::= E*E E ::= E=E E ::= Num | true | false
where Num represents integers.
a) Consider the generalized CYK algorithm from
- Lecturecise 11, slide 3
Run the algorithm on input:
1=2*3=true
checking whether it can be parsed. Show the content of the 'chart', that is, the set of triples 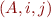 , after the algorithm finishes.
, after the algorithm finishes.
b) How many parse trees can you extract from this chart?
c) Write down those parse trees that are correct according to the following types:
+ : Int x Int→Int
* : Int x Int→Int
= : Bool x Bool → Bool
= : Int x Int → Bool
d) Can you modify the CKY algorithm following the ideas from:
- Lecturecise 12, slide 5-8
to introduce a semantic function  that computes only those trees that are correct according to the above types of operators?
that computes only those trees that are correct according to the above types of operators?
e) What does the new algorithm return on the above input?
Problem 3
Consider the following class:
class Rectangle {
var width: Int
var height: Int
var xPos: Int
var yPos: Int
def area: Int = {
if(width > 0 && height > 0)
width * height
else
0
}
def resize(maxSize: Int) {
while(area > maxSize) {
width = width / 2
height = height / 2
}
}
}
a) Determine the environment of this class.
b) By giving the type derivation trees for each method show that this class type checks.
Problem 4
Determine if the following piece of codes type check according to the type rules.
Show all steps and give type derivation trees where applicable.
a) The class Array has a field length in which the length of the array is stored.
def swap(lst: Array[Int], a: Int, b: Int): Array[Int] = {
if (a >= lst.length || b >= lst.length) lst else {
val swap = lst(a)
lst(a) = lst(b)
lst(b) = swap
lst
}
}
b)
Recall that we have the two type rules:
- If
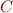 is a declared subclass of
is a declared subclass of 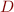 , then
, then 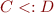
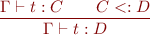
i) Give the type rule corresponding to new.
ii) Show this code typechecks.
class Shape
class Rectangle(width: Int, length: Int) extends Shape {
def area : Int = width * length
}
class Square(length: Int) extends Rectangle(length,length)
new Square(5).area