This is an old revision of the document!
Regular Expressions and Automata with Parallel Inputs
Given an alphabet 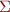 , we consider a larger (but still finite) alphabet
, we consider a larger (but still finite) alphabet  for some
for some 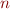 . Keep in mind that
. Keep in mind that 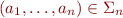 is just one symbol; we often write it as
\[\left(
is just one symbol; we often write it as
\[\left(
\begin{array}{l}
a_1 \\
\ldots \\
a_n
\end{array}
\right)
\]
We can consider
- regular expression
- automata
on such alphabets.
Using Propositional Formulas to Denote Finite Sets of Symbols
Suppose 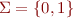 .
.
Let  .
.
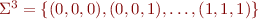 .
.
Language representing that the third coordinate is the logical and of the first two is: \[
\left(
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
\end{array}
\right)
+
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
0 \\
1 \\
0 \\
\end{array}
\right)
+
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
1 \\
0 \\
0 \\
\end{array}
\right)
+
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
1 \\
1 \\
1 \\
\end{array}
\right)
\right)^*
\]
Instead of considering  , we can consider
, we can consider 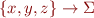 where
where 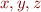 are three names of variables.
are three names of variables.
We then use propositional formulas to denote possible values of bits. For example, ![Math $[x \land y]$](/w/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img954c0a8204c8aa9660aebfc1051cfcb9.png) denotes the regular expression
\[
denotes the regular expression
\[
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
1 \\
1 \\
0 \\
\end{array}
\right)
+
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
1 \\
1 \\
1 \\
\end{array}
\right)
\] The bitwise and relation, shown above, is given by \[
[z \leftrightarrow (x \land y)]^*
\]
In general
![Equation \begin{equation*}
[p(v_1,\ldots,v_n)] =
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
a_{11} \\
\ldots \\
a_{1n}
\end{array}
\right)
+ \\
\ldots \\
+ \\
\left(
\begin{array}{l}
a_{k1} \\
\ldots \\
a_{kn}
\end{array}
\right)
\end{equation*}](/w/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img9a7018c4d524d35b6df7b0d7c888b50d.png)
where 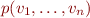 is a propositional formula and
is a propositional formula and 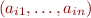 for
for 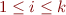 are all tuples of values of propositional variables for which
are all tuples of values of propositional variables for which 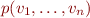 is true.
is true.
Notational advantage: the set of variables can be larger, the expression is still the same.