This is an old revision of the document!
Expressing finite automaton in MSOL over strings
Consider a finite automaton with alphabet 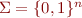 , states
, states 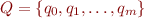 , transition relation
, transition relation  , initial state
, initial state 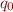 and final states
and final states  .
.
Let the sets 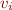 denote the encoding of input string of the automaton.
denote the encoding of input string of the automaton.
There exists an execution of an automaton iff there exist the intermediate states given by transition relation  . We describe intermediate states using sets
. We describe intermediate states using sets 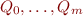 , one for each state of the in
, one for each state of the in  . The state
. The state  is the set of positions in the execution at which the automaton is in state
is the set of positions in the execution at which the automaton is in state 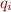 . We encode the transition relation
. We encode the transition relation  using the formula
using the formula
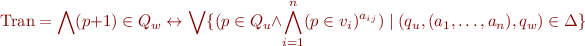
Initially, the automaton is in the initial state:
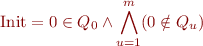
and at some final position 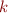 it should be in final state:
it should be in final state:
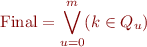
To express the property that an automaton accepts a string whose length is given by free variable  we then use formula
we then use formula  :
:
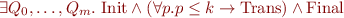
Then the word is accepted if the above formula holds for the entire input \[
\exists k. (F \land \forall p. k < p \rightarrow \bigwedge_i p \notin v_i)
\]